Male Breast Reduction (Gynecomastia)
If you are guy who struggles with excess breast tissue or “puffy” nipples, you may feel self-conscious taking your shirt off in public—or even wearing tight-fitting shirts. You have likely found that even with a regular diet and exercise routine, male breast tissue is difficult to shrink. If this sounds familiar, then you may benefit from male breast reduction surgery. Regardless of the cause your excess breast tissue, board certified plastic surgeon Dr. Brannon Claytor is able to tailor a fully customized surgical plan to your needs to restore a flat, masculine chest—and your confidence.
What is gynecomastia, and what causes it?
Gynecomastia is the overdevelopment of male breasts. This is a quite common condition characterized by an excess of localized fat and/or glandular tissue in the breast. It is sometimes caused by disease, hormonal changes, heredity or certain medications, although, in most cases, its cause is unknown. It can occur in one or both breasts, and can affect babies, preteens, teenagers and grown men. Symptoms of gynecomastia include enlarged breasts, breasts that feel rubbery or firm and (in young boys) nickel- or quarter-sized breast “buds.” (Breast buds are common in adolescents, and tend to go away on their own.)
Dr. R. Brannon Claytor
Dr. Claytor is board certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery and holds over 15 years of experience as a cosmetic plastic surgeon. An innovator and teacher in the field of plastic surgery, he uses advanced techniques like the drain-free tummy tuck and deep plane facelift to streamline recovery and provide natural-looking, durable results.
How is gynecomastia treated?
As long as breast development is complete, male breast reduction surgery can be used to treat gynecomastia that is not caused by disease or medication. Treatment choices include liposuction or surgery to remove enlarged tissues, or a combination of the two; which technique is chosen depends on the amount and type of tissue in the breasts.
- If the breasts consist mostly of fatty tissue, liposuction can be used alone to suction out fat through very small incisions made in the nipples or underarm areas.
- For breasts with an excessive amount of glandular tissue, excision surgery will need to be performed to manually cut away excess fat, skin, and tissue; surgical excision requires a larger incision (than is used with liposuction) placed around the edge of the nipple-areola complex.
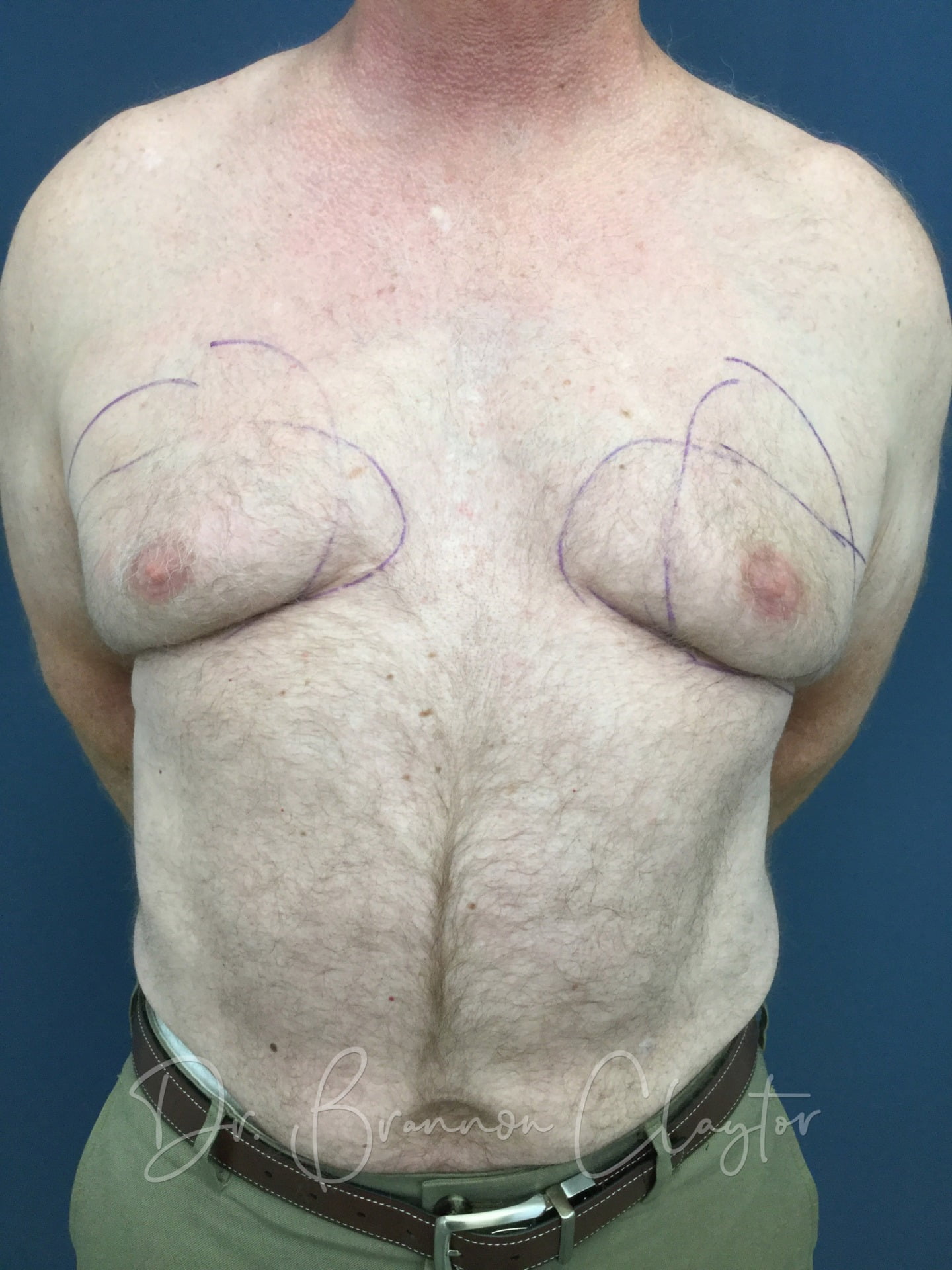
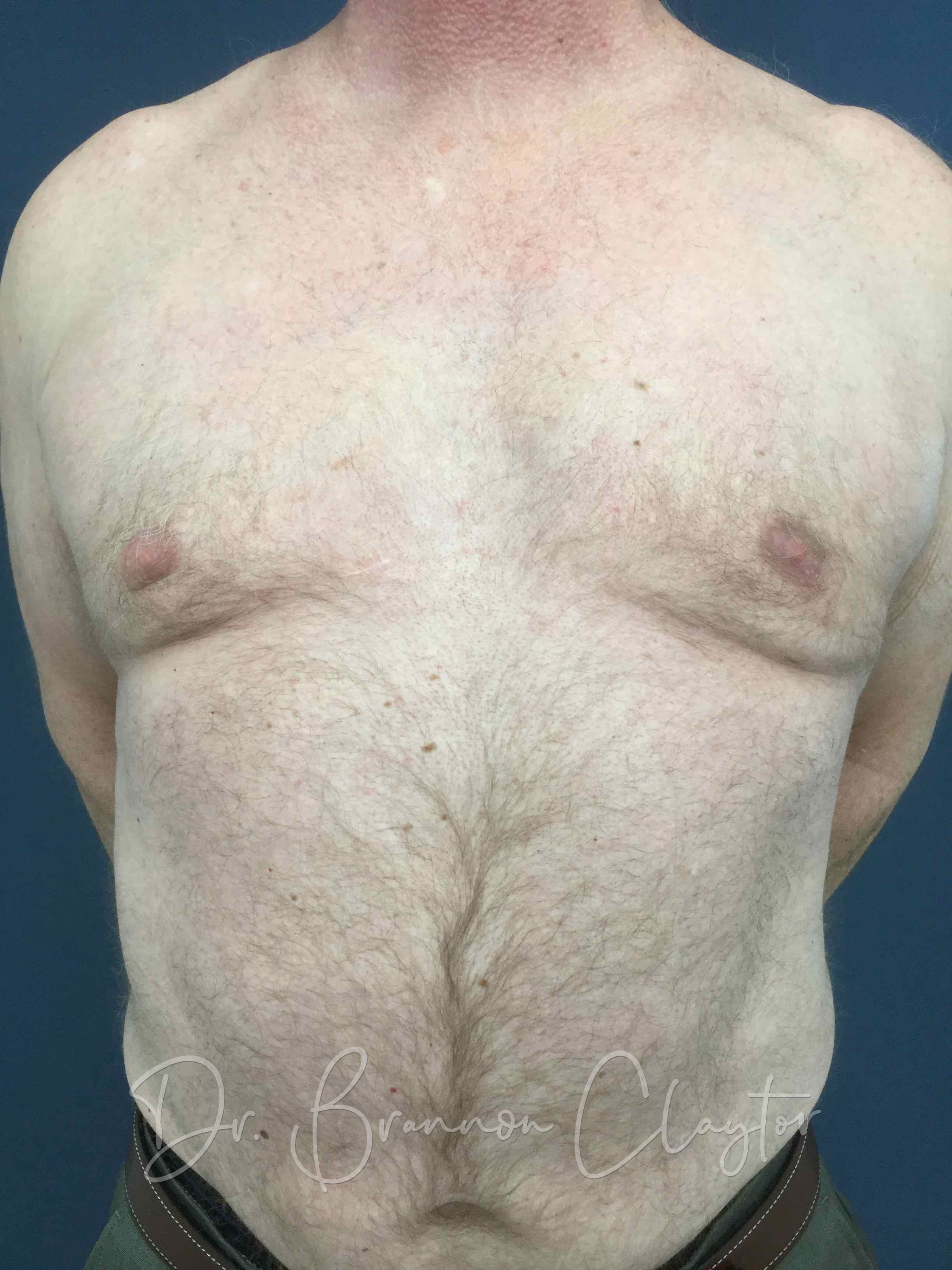
This Patient with excess male breast tissue, or gynecomastia, is pictured here before and after male breast reduction surgery with Philadelphia plastic surgeon Dr. Brannon Claytor.
*Individual results may vary.
Am I a good candidate for male breast reduction surgery?
To be a good candidate for this procedure, you should be in good health for surgery and agree with the following:
- You are a non-smoker
- You are at a stable weight you plan to maintain
- You have enlargement in either one or both sides of your chest
- You desire a change in your chest appearance.
If you are unsure whether or not your symptoms may benefit from male breast reduction surgery, we encourage you to set up a consultation with Dr. Claytor at our Bryn Mawr office. Dr. Claytor will be happy to talk with you and learn about your concerns, discuss what results he can achieve for you, and share before and after photos of his previous male breast reduction patients so that you can understand what results are possible with this procedure.
- Key Benefits
- Glossary
- Flatter chest: Removal of excess breast tissue and fat results in a flatter, firmer, and more masculine chest contour.
- Improved comfort: Reduces physical discomfort and skin irritation caused by enlarged breasts, facilitating ease in movement and exercise.
- Expanded wardrobe choices: Men can wear fitted clothing and swimwear with greater comfort and confidence, without feeling self-conscious about their appearance.
- Long-lasting solution: Provides long-lasting resolution to gynecomastia, especially when combined with a healthy lifestyle.
Gynecomastia: Abnormal enlargement of male breast tissue.
Liposuction: Surgical technique used to remove excess fat from specific areas of the body.
Mastectomy: Surgical removal of breast tissue.
Excision: Surgical removal of tissue.
Areola: Pigmented skin surrounding the nipple.
Inframammary Fold (IMF): The crease beneath the breast.
Anesthesia: Medication used to prevent pain during surgery.
General Anesthesia: Medication that induces unconsciousness for the duration of surgery.
Local Anesthesia: Medication that numbs a specific area without causing unconsciousness.
Sedation: Medication that induces relaxation and drowsiness.
Drainage: Removal of excess fluid from the surgical site.
Hematoma: Collection of blood outside of blood vessels, potentially occurring after surgery.
Seroma: Accumulation of serous fluid at the surgical site.
Compression Garment: Tight-fitting clothing worn to reduce swelling after surgery.
Scar Revision: Surgical technique used to minimize the appearance of scars.
Cannula: Thin tube used during liposuction to remove fat.
Incision: Cut made during surgery to access the surgical site.
Post-operative Care: Care and instructions given to patients following surgery.
Recovery Period: Time needed for the body to heal following surgery.
Invasive Surgery: Surgical procedures that penetrate the skin and underlying tissues.
Non-invasive Procedure: Treatment that doesn’t require incisions or penetration of the body.
Adipose Tissue: Body fat.
Pseudogynecomastia: Enlargement of male breasts due to fat accumulation rather than glandular tissue.
Biopsy: Removal and examination of tissue to diagnose or exclude certain conditions.
Hormone Therapy: Treatment involving the modulation of hormone levels in the body.
Schedule your gynecomastia surgery consultation with Dr. Brannon Claytor
Philadelphia board certified plastic surgeon Dr. R. Brannon Claytor has over 15 years of experience offering cosmetic plastic surgery procedures. At Claytor Noone Plastic Surgery, he served patients from Philadelphia, Bryn Mawr, Main Line, and the surrounding areas. A member of The Aesthetic Society’s Board of Trustees, the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS), and a Fellow of the American College of Surgeons (FACS), Dr. Claytor is dedicated to continuously advancing his surgical techniques and teaching his methods to colleagues at national meetings. In addition to his surgical work, Dr. Claytor the Chief of Plastic Surgery for Main Line Health Systems, and is a Clinical Associate Professor at Lankenau Institute of Medical Research.
To learn if plastic surgery to treat gynecomastia is right for you, or to get answers to your questions, please call our Bryn Mawr office at (610) 527-4833 or contact us online to schedule a consultation with Dr. Claytor. We look forward to helping you reach your goals.
References »
Sansone A, Romanelli F, Sansone M, Lenzi A, Di Luigi L. Gynecomastia and hormones. Endocrine. 2017 Jan;55(1):37-44. doi: 10.1007/s12020-016-0975-9.
Soliman AT, De Sanctis V, Yassin M. Management of Adolescent Gynecomastia: An Update. Acta Biomedica. 2017 Aug 23;88(2):204-213. doi: 10.23750/abm.v88i2.6665.
Johnson RE, Kermott CA, Murad MH. Gynecomastia – evaluation and current treatment options. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management. 2011;7:145-8. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S10181.
Taheri AR, Farahvash MR, Fathi HR, Ghanbarzadeh K, Faridniya B. The Satisfaction Rate among Patients and Surgeons after Periareolar Surgical Approach to Gynecomastia along with Liposuction. World Journal of Plastic Surgery. 2016 Sep;5(3):287-292.
Areas Served:

Medically reviewed by Dr. R. Brannon Claytor — Updated on Feb 20, 2024


